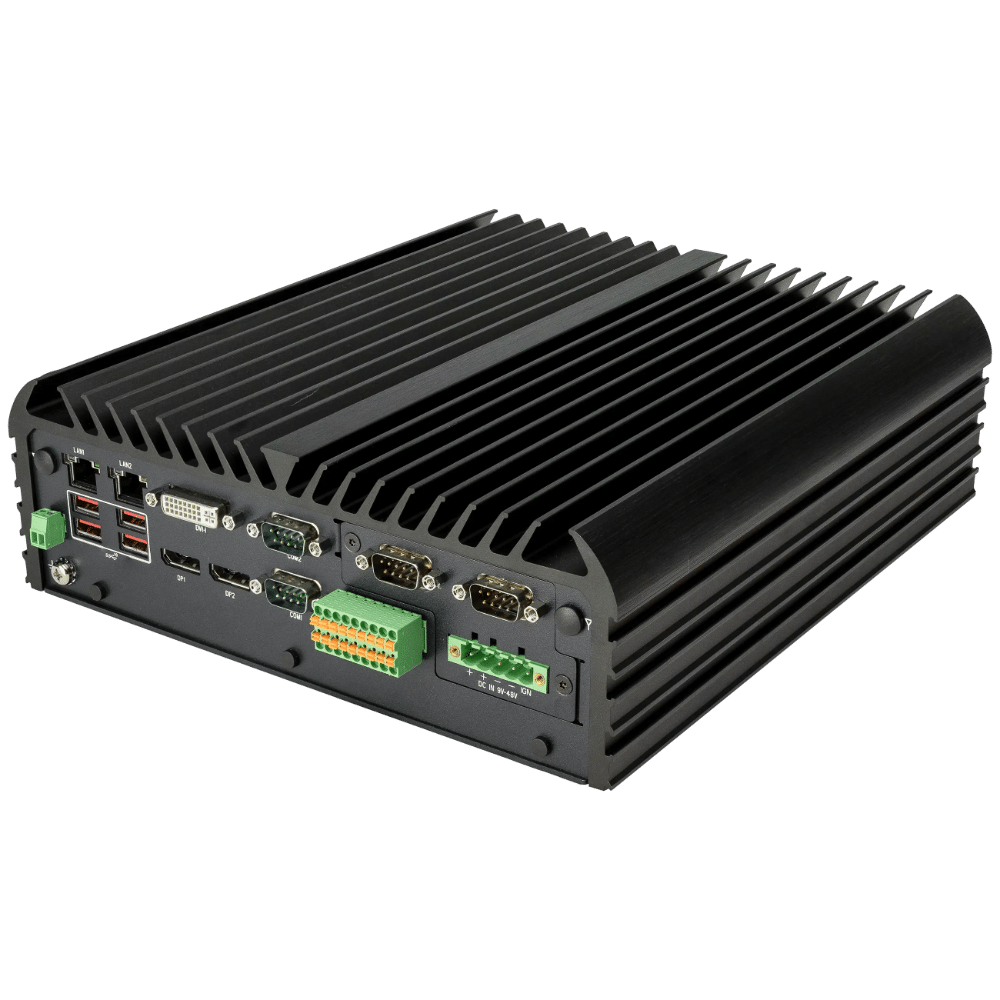
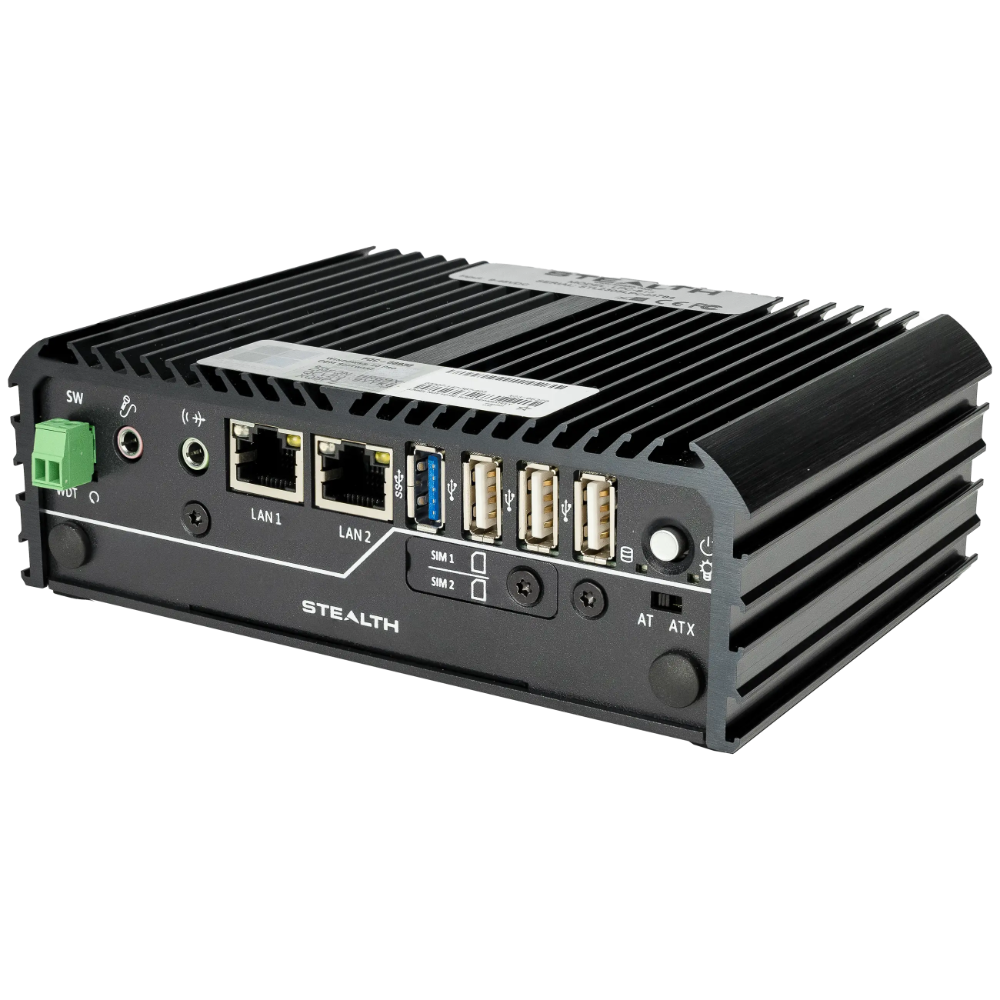
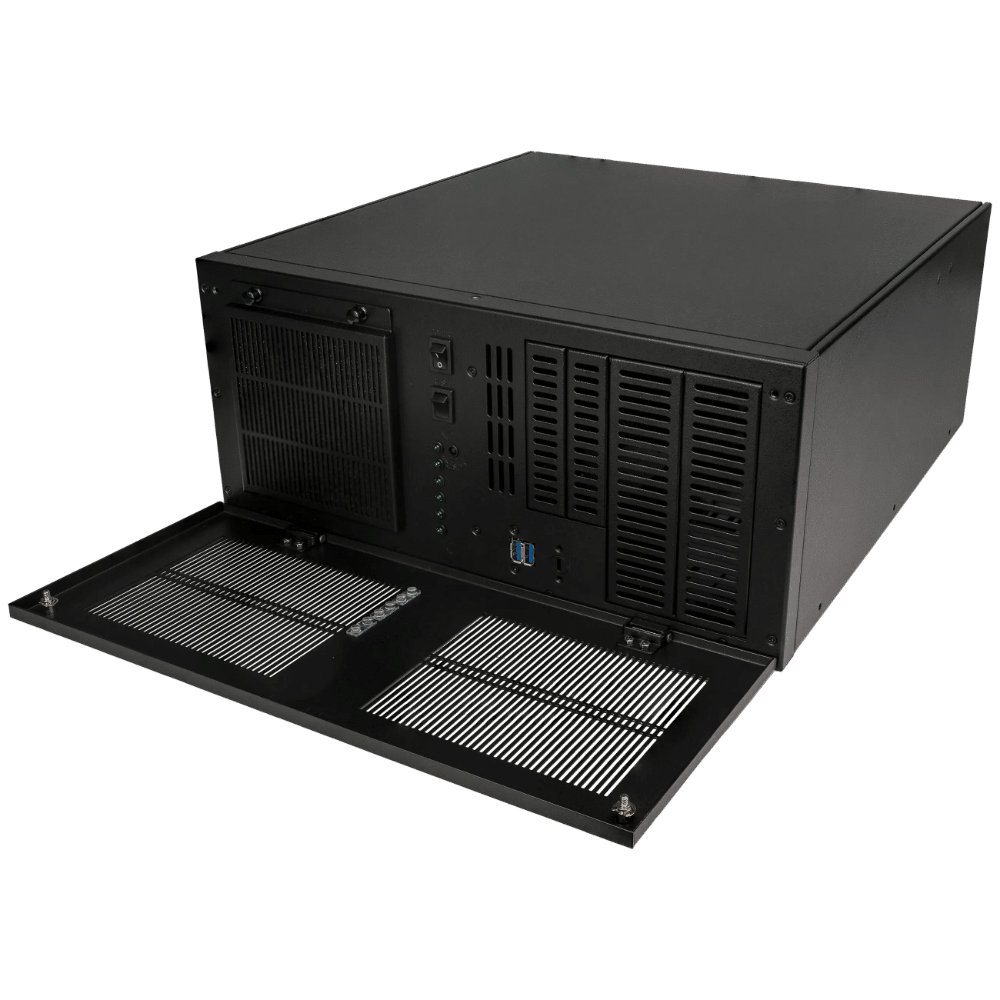
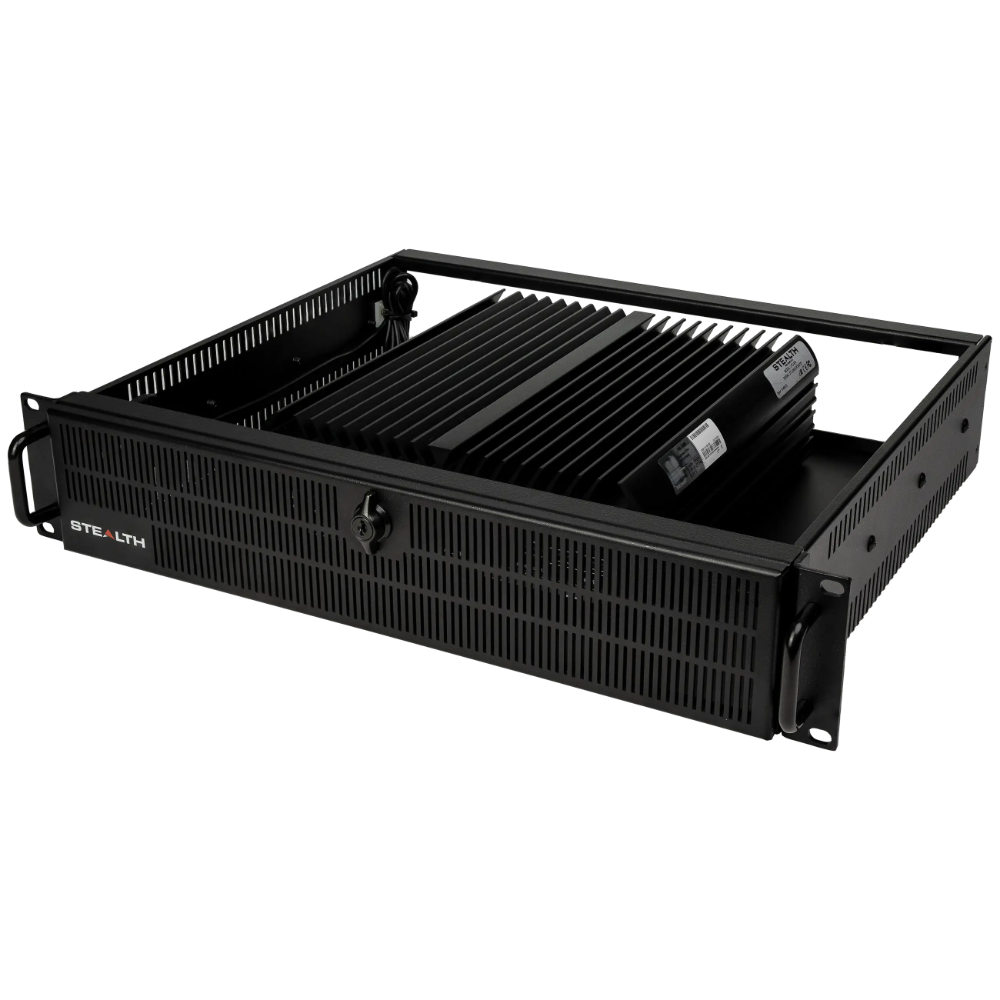
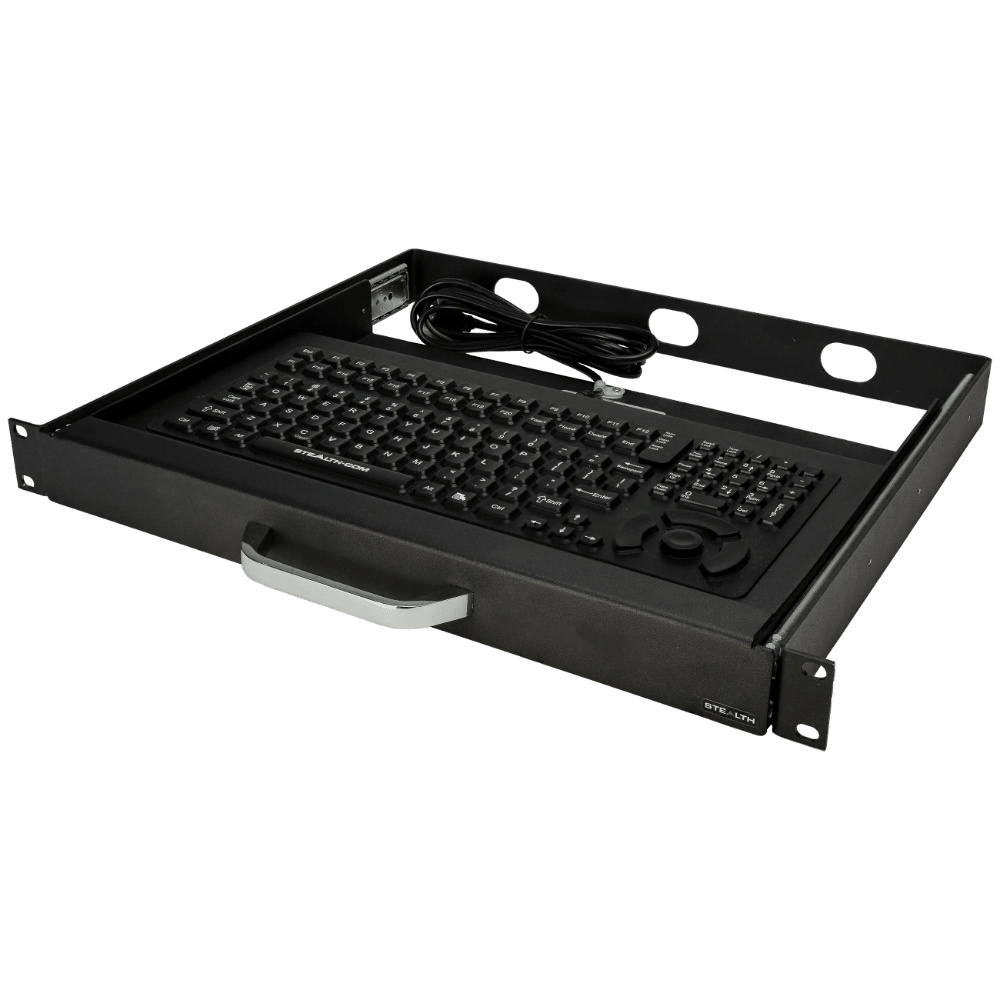
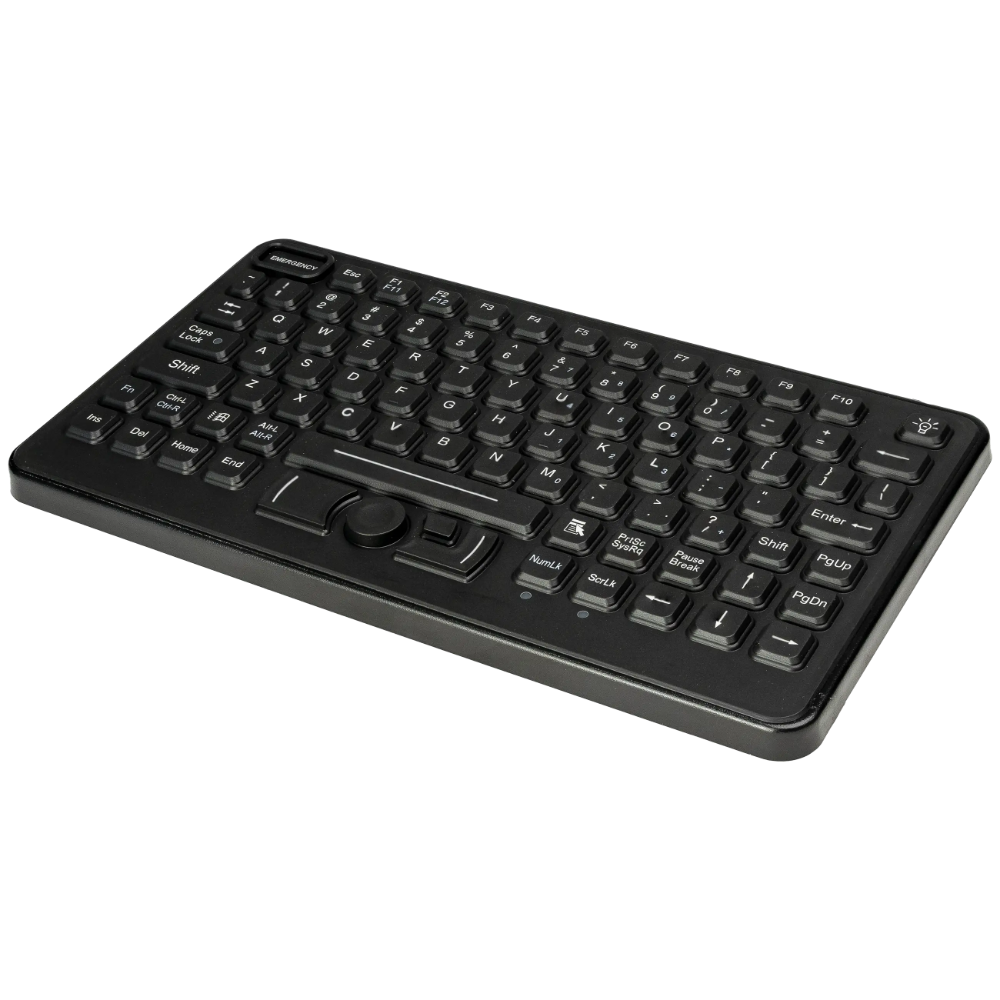
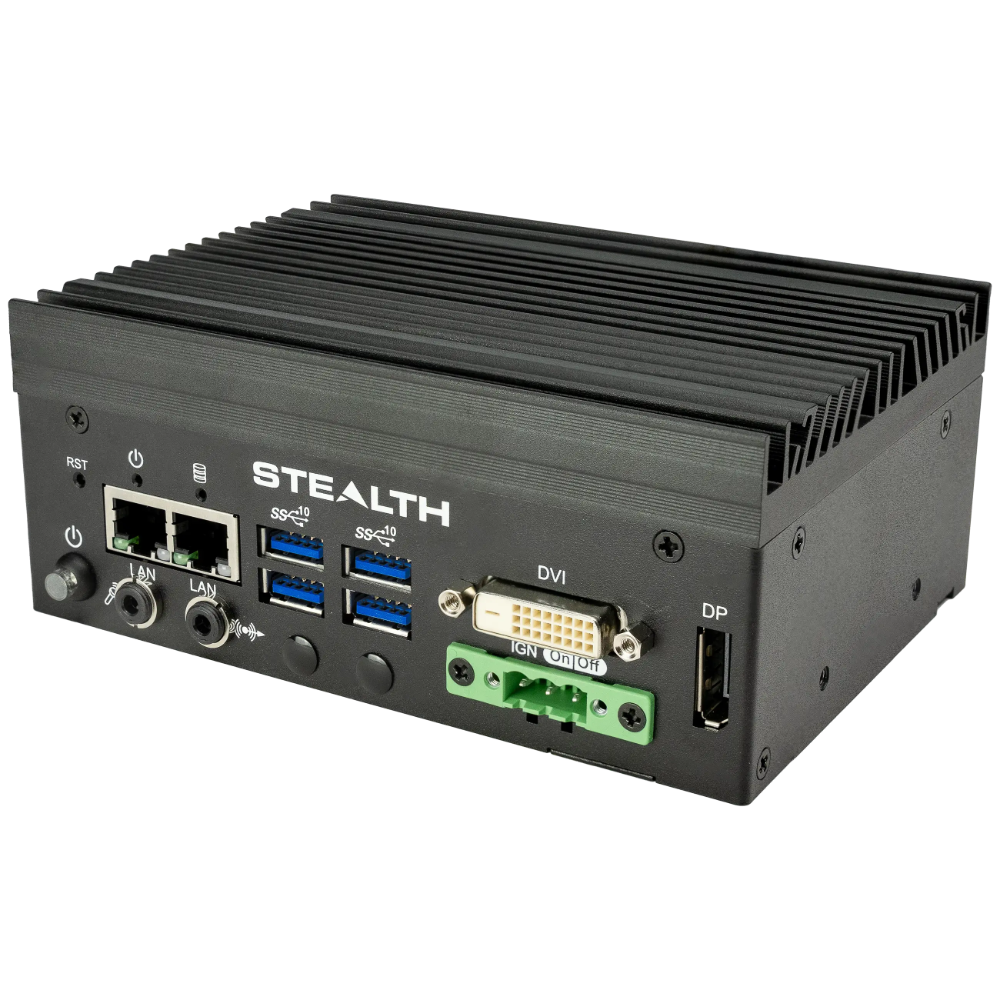
Stealth’s LPC-400 series offers high-performance Mini PCs with extensive I/O options. The LPC-800 series boasts a rugged, fanless, modular design for tough environments. Meanwhile, the LPC-900 series supports up to 7 displays with 8K resolution, embodying versatility and top-tier technology across our Standard Series.
Case Study by Industries & Applications
Get a closer look at our world of rugged innovation and specialized solutions through our case studies. Discover how our cutting-edge products have transformed challenges into success stories across diverse industries and applications.
Selected: All
( Showing: 3 of 3)
Stay Connected
Have questions or need assistance?
Contact us today and discover how our rugged solutions can support your needs.
Stay ahead with the latest innovations—subscribe to our monthly newsletter for news, promotions, and exclusive updates delivered straight to your inbox.